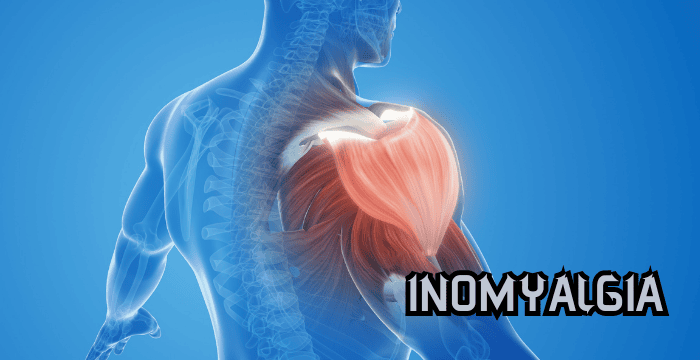
Inomyalgia is a condition characterized by muscle pain, stiffness, and discomfort, often affecting daily movement and overall quality of life. While it may sound similar to other muscle-related disorders, inomyalgia has its own clinical presentation and management approach. Understanding how inomyalgia is treated and managed is essential for reducing symptoms, improving mobility, and preventing long-term complications.
This article provides a complete analysis of inomyalgia treatment and management, focusing on medical approaches, lifestyle adjustments, physical therapies, and long-term care strategies.
Understanding Inomyalgia
Inomyalgia primarily involves pain within muscle tissue, often caused by inflammation, overuse, strain, or underlying systemic conditions. Symptoms may range from mild soreness to persistent muscle pain that interferes with normal activities.
Common symptoms include muscle tenderness, stiffness after rest, fatigue, reduced flexibility, and discomfort that worsens with movement or stress. Because symptoms can overlap with other muscle disorders, accurate assessment is important before starting treatment.
Goals of Inomyalgia Treatment
The primary objectives of treating inomyalgia are not limited to pain relief alone. A comprehensive treatment plan focuses on multiple goals:
- Reducing muscle pain and inflammation
- Restoring normal movement and flexibility
- Preventing muscle stiffness and weakness
- Improving daily function and comfort
- Addressing underlying causes or triggers
Successful management often requires a combination of medical care and self-management strategies.
Medical Treatment Options
Medical treatment for inomyalgia depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s overall health.
Pain Relief and Anti-Inflammatory Support
Doctors may recommend medications that help reduce inflammation and manage pain. These are usually prescribed for short-term relief, especially during flare-ups. Proper dosage and duration are important to avoid side effects. Testosterone
In more persistent cases, muscle relaxants may be considered to ease tension and reduce spasms. These medications help muscles recover and improve comfort during movement.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
If inomyalgia is linked to another medical condition such as infection, autoimmune disorders, or metabolic imbalances, treatment focuses on managing the root cause. Proper diagnosis plays a key role in long-term symptom control.
Physical Therapy and Movement Management
Physical therapy is one of the most effective non-drug approaches to managing inomyalgia. Guided exercises help improve muscle strength, flexibility, and circulation.
A trained therapist may design a program that includes gentle stretching, controlled strengthening exercises, and posture correction. These activities help prevent muscle stiffness and reduce the likelihood of recurring pain.
Regular movement, even at low intensity, is essential. Prolonged inactivity often worsens muscle pain and stiffness, making recovery slower.
Lifestyle Modifications for Symptom Control
Lifestyle changes are a critical part of long-term inomyalgia management. Small adjustments can significantly reduce muscle strain and discomfort.
Maintaining a balanced routine that includes adequate rest, proper sleep, and stress management helps muscles recover more effectively. Chronic stress is known to increase muscle tension, which can intensify pain.
Proper hydration and balanced nutrition also support muscle health. Muscles require essential nutrients and fluids to function optimally and repair minor damage.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are commonly used to manage muscle pain associated with inomyalgia.
Warm compresses or heating pads help relax tight muscles and improve blood flow, making them especially useful for stiffness. Cold therapy, on the other hand, helps reduce inflammation and numb sharp pain, particularly after physical activity.
Alternating between heat and cold may provide additional relief for some individuals, depending on symptom patterns.
Exercise and Activity Management
While rest is important during severe pain episodes, complete inactivity is not recommended. Controlled physical activity helps prevent muscle weakening and stiffness.
Low-impact exercises such as walking, stretching, or gentle mobility routines support muscle health without excessive strain. Overexertion should be avoided, as it can worsen symptoms.
Listening to the body and pacing activities appropriately is key to long-term improvement.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Chronic muscle pain can affect mental well-being, leading to frustration, anxiety, or low mood. Emotional stress can further amplify muscle tension and pain perception.
Relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, or guided relaxation can help reduce stress-related muscle tightness. In some cases, professional counseling may be beneficial for individuals struggling with persistent pain.
Long-Term Management and Monitoring
Inomyalgia often requires ongoing management rather than a one-time treatment. Regular monitoring of symptoms helps identify triggers and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Keeping track of physical activity, stress levels, and pain patterns allows individuals to make informed decisions about their routines. Periodic medical evaluations ensure that symptoms are properly managed and that no underlying condition is overlooked.
Consistency is essential. Long-term success depends on maintaining healthy habits and following recommended therapies even when symptoms improve.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Medical attention should be sought if muscle pain becomes severe, persistent, or progressively worse. Symptoms such as unexplained weakness, swelling, fever, or pain that does not respond to basic treatment require professional evaluation.
Early intervention often prevents complications and shortens recovery time.
Conclusion
Inomyalgia treatment and management focus on a balanced, multi-approach strategy that combines medical care, physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and long-term monitoring. While muscle pain can be disruptive, proper management allows most individuals to regain comfort, mobility, and daily function.
By addressing both symptoms and underlying causes, individuals with inomyalgia can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of recurring pain. Consistency, awareness, and proactive care remain the foundations of successful inomyalgia management.